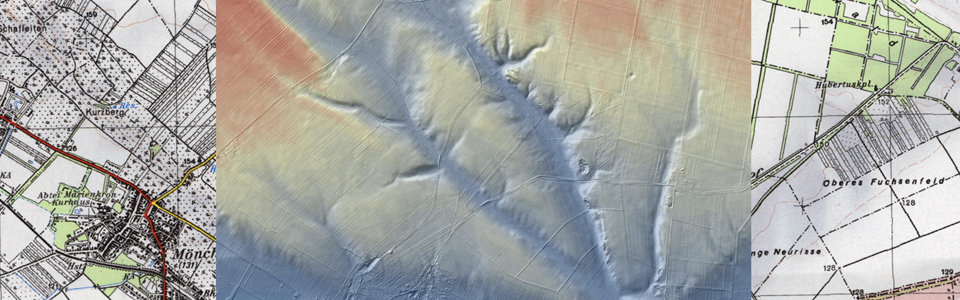
Airborne laser scanning (ALS)
Over the past few years, airborne laser scanning (ALS) has turned out to be a potential tool for recognition and measurement of archaeological features that survived in the topography in open and wooded areas. ALS results in a precise model of the surface, however, there is no way to detect buried features or sites that have not left traces in the relief using this method. While archaeological applications of ALS are increasing, they are still often restricted to non-forested areas. Due to its ability to measure the ground under a vegetation canopy, ALS has a major impact in the archaeological reconnaissance of vegetated areas. To extend aerial archaeology with state-of-the-art ALS and to develop the application of ALS for archaeological prospection is one promising and challenging task that is investigated by the LBI-ArchPro.
Full-waveform (FWF) ALS systems have considerable advantages for the generation of digital terrain models (DTM) in vegetated areas, as the FWF-parameters might improve classification of ALS data into terrain and off-terrain points, resulting in improved DTM quality and a higher potential for the subsequent archaeological interpretation. As FWF-ALS displays a great potential, but still is in its infancy (in contrast to conventional ALS sensors, FWF-ALS is just available since a few years), several key topics, such as the evaluation of the data acquisition time-frame, and various techniques for advanced classification of the acquired point cloud, are being investigated.